Quality matters when hiring for a big project. Call a Best Pick now!
Different Types of Heating Systems for Your Home (Part 1 of 2)
February 5th, 2013 byHome heating systems have come a long way since the humble fireplace, and while technological advances and new options have made heating your home more efficient than ever, the number of choices available today can make selecting a heating system seem daunting.
However, knowing more about different kinds of heaters on the market as well as their advantages and disadvantages will help you assess which system is better for your home and make your decision an easier one.
Furnaces
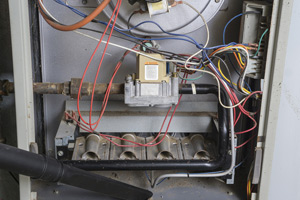
Furnaces are one of the most common home heating systems, and they work by blowing heated air through a duct system. Furnaces are typically referred to as “forced-air” heating systems and can run on different types of fuel, but natural gas, oil, and electricity are the most common sources of energy currently available.
Furnaces are more energy efficient than ever, but their cost varies based on fuel rates, electricity prices, and energy costs. However, if you don’t need to replace your furnace due to age or malfunction, you can call a professional to have your existing unit retrofitted to be more energy efficient.
Look for an AFUE rating of at least 80, and keep in mind that the higher the AFUE number, the more money you’ll save on heating bills in the future—but you may find the initial investment greater than other options.
- Advantages: Widely available; increasingly more energy efficient; aid in the cooling of your home during warmer months; can be retrofitted to clean the air in your home.
- Disadvantages: Require ducts; natural gas could be dangerous if leaks occur.
Boilers and Radiant Heating Systems

Though sometimes the term “boiler” is used interchangeably with “furnace,” they are very different types of systems. Boilers heat water via natural gas, electricity, or propane—although the water doesn’t boil, as the name implies.
As opposed to the forced air of the furnace system, most boilers move heat into your home through a radiant heating system like traditional radiators, baseboard heaters, or aluminum panels in a home’s floors, walls, or ceilings.
Radiant floor heat is the most popular option, and it works best when paired with ceramic tile as the floor covering. Since it transfers heat without using air ducts, a boiler and radiant heating system can heat your home without circulating allergens throughout the house.
Though the cost of boiler installation can be higher than a furnace, they are as energy efficient as their dry-heat cousin. Like furnaces, an older and functional boiler can be retrofitted by a professional to be more energy efficient.
- Advantages: Non-allergenic heat; very energy efficient; increasing popularity in the US; radiant heating systems can be controlled room-to-room and take up less space than duct systems.
- Disadvantages: More expensive installation (copper pipes are usually used); air conditioning system must be added separately; some technicians do not service boilers.
Heat Pumps

Heat pumps use refrigerant to absorb heat from outside sources—like the air, the ground, or even a body of water—and then use a heat exchanger to transfer it inside. (The exchange of heat can also be reversed to cool a home.)
The most common kinds of heat pumps draw thermal energy from ambient air or the ground. Heat pumps, in general, are becoming increasingly popular heating choices for homeowners.
Although air-source and ground-source heat pumps may be more expensive than conventional heating systems, they can provide significant energy savings to homeowners who live in temperate climates.
- Advantages: Highly energy efficient; can be run year-round to heat and cool; can provide further savings with water bills if fitted with a desuperheater, an add-on that transfers excess heat to a hot water tank.
- Disadvantages: Can be strained in extreme temperatures; ground-source heat pumps can be expensive to install; could have reduced energy efficiency depending on the amount and type of the land surrounding your home; become inefficient when used below 32 degrees ambient temperature.
Heating systems will affect how you feel in your home during the cold months as much as they’ll affect your pocketbook. Before picking a brand or even an installation company, it’s a good idea to answer some questions about what you want out of your heater.
How much heat do you want your system to produce? How extreme are your winters? How important is energy efficiency to you? By answering questions like these and hiring a quality heating and air conditioning company, you’ll ensure that you don’t wake up with a cold nose when the temperature drops each winter.
Read about three important tips to keep in mind when choosing your next heating system.


























